Neodymium magnets, or NdFeb magnets as they are scientifically known, come in a diverse array of shapes and sizes. Each unique shape has its own set of potential magnetization orientations.
The magnetic force of a magnet is most potent when its pole directly contacts a surface of the opposite polarity. For example, a disc or ring magnet with axial magnetization performs optimally when one of its flat surfaces is in direct contact with the flat surface of another disc or ring magnet of opposite polarity. However, this doesn’t imply that the magnet lacks magnetic pull on its sides, rather, it’s just not as powerful when deployed in such a manner.
Understanding the magnetization direction of your magnets can greatly aid in identifying the most suitable magnet for your needs. It can also assist you in determining the ideal orientation for the magnet to function at its peak efficacy.
Disc and Cylinder Magnets
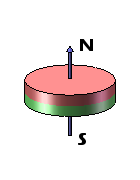
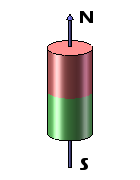
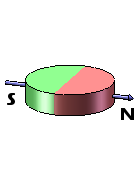
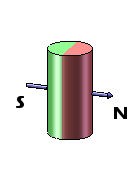
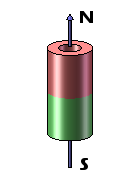
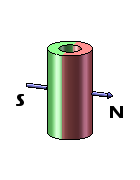
Disc magnets exhibit two types of magnetization – axial and diametrical. In the case of axially magnetized disc magnets, the poles are situated on the broad, flat faces of the magnet. Conversely, for diametrically magnetized disc magnets, the poles are located on the curved sides of the disc.
| Axially Magnetized Disc Magnets | Axially Magnetized Cylinder Magnets | Diametrically Magnetized Disc Magnets | Diametrically Magnetized Cylinder Magnets |
 |  |  |  |
Block Magnets
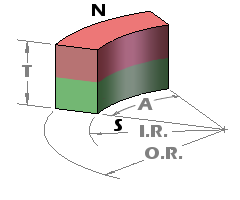
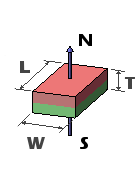
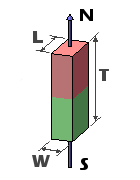
Block magnets are characterized by three measurements: Length, Width, and Thickness. To maintain consistency, we define the Thickness dimension as being along the axis of magnetization. While the thickness is typically the smallest dimension, there are exceptions!
Occasionally, we receive inquiries about block magnets magnetized through the length or width. Indeed, we offer a selection of elongated “bar” magnets, where the magnetization occurs along the lengthiest dimension. However, we still refer to this dimension as the Thickness for the sake of consistency.
| Magnetized Through Thickness | Magnetized Through Thickness |
 |  |
Ring Magnets
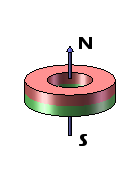
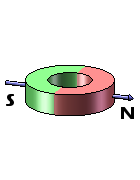
Ring magnets possess two distinct forms of magnetization – axial and diametrical. In axially magnetized ring magnets, the north and south poles are present on the flat surfaces of the ring. Conversely, diametrically magnetized ring magnets feature their north and south poles on the circular sides of the ring.
| Axially Magnetized Ring Magnets | Axially Magnetized Ring Magnets | Diametrically Magnetized Ring Magnets | Diametrically Magnetized Ring Magnets |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Arc Magnets
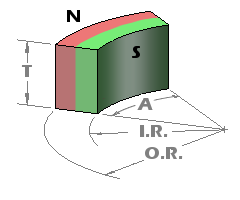
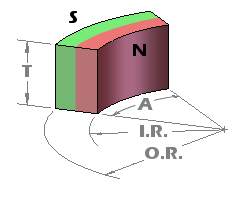
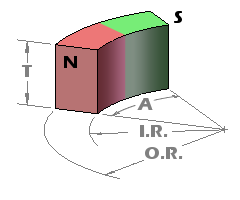
Arc Segment magnets, known for their unique curved shape, offer versatility with four possible directions of magnetization. This allows for a range of application-specific orientations to best suit various project requirements.
| North on the Outside Face | South on the Outside Face | Magnetized through Circumference | Magnetized through Thickness |
 |  |  |
|
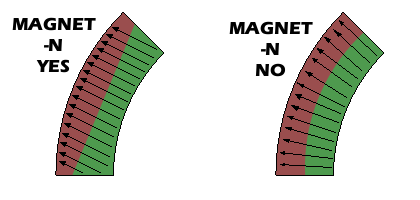
It’s important to understand that the magnetization of these Arc Segment magnets occurs along a linear axis, and it’s not genuinely radial. This means that the lines of magnetization do not converge towards the arc’s center. However, when these arc segments are assembled together, they can serve as an effective approximation of a radially magnetized ring, making them versatile components in a variety of applications.
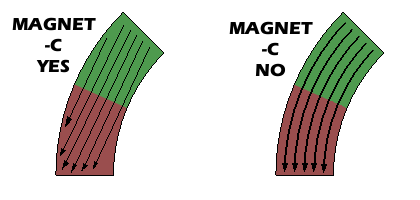
For circumferential magnetization of Arc Segment magnets, the magnetization lines remain parallel to one another. They do not follow the curve of the arc, but rather maintain a straight path, reinforcing the fact that magnetization isn’t truly radial or curved in nature, even in the case of these uniquely shaped magnets.
| Arc Magnetization with Poles on Inner & Outer Face | Circumferential Magnetization of Arc Segments |
 |  |
Sphere Magnets
Neodymium sphere magnets, due to their symmetrical spherical shape, have a unique property: they can only be axially magnetized. This means that the magnetic poles are located on opposite sides of the sphere, creating a straight line or “axis” through the center of the magnet.
| Axially Magnetized Sphere Magnets |
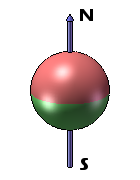 |
Mounting Magnets
Round Mounting Magnets are carefully constructed by placing an axially magnetized disc or ring magnet within a robust steel cup. In this setup, the north pole of the magnet is oriented to face outward.
Similarly, our Rectangular Mounting Magnets adhere to the same construction design, with an axially magnetized magnet, but in this case, typically a block or rectangular shape, enclosed within a steel frame.
| North Pole Facing Out |
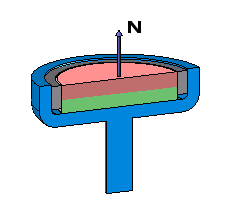 |